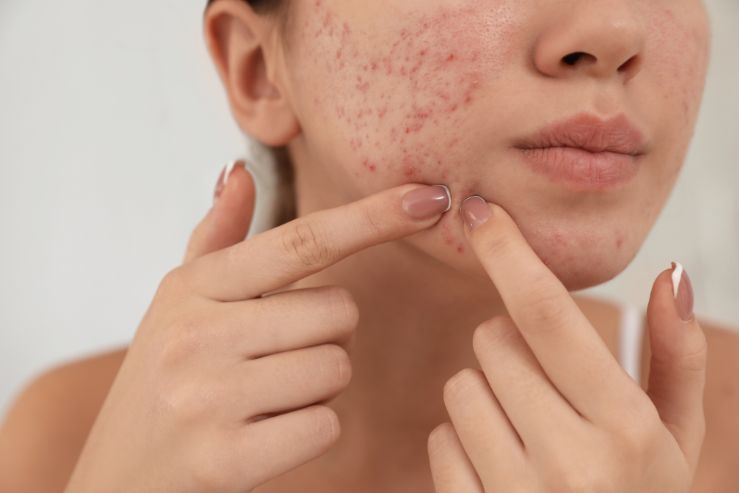
Acne is a common skin condition characterized by pimples, blackheads, whiteheads, cysts, and nodules. It occurs when hair follicles become clogged with oil and dead skin cells, leading to inflammation and sometimes bacterial infection. Factors such as hormonal changes, genetics, diet, stress, and certain medications can contribute to acne development.
Topical Treatments: Prescription creams, gels, or lotions containing ingredients like benzoyl peroxide, retinoids, or antibiotics to reduce bacteria, oil production, and inflammation.
Oral Medications: Antibiotics or hormonal treatments may be prescribed for moderate to severe acne to reduce inflammation and control bacteria.
Chemical Peels: Application of a chemical solution to exfoliate the skin, unclog pores, and reduce acne blemishes. Peels may contain salicylic acid, glycolic acid, or other exfoliating agents.
Laser and Light Therapies: Advanced treatments using lasers or intense pulsed light (IPL) to target acne-causing bacteria and reduce oil production. These therapies can also improve skin texture and reduce acne scars.
Extraction: Manual removal of blackheads and whiteheads by a dermatologist using sterile instruments to prevent further inflammation and scarring.
Cryotherapy: Freezing of acne lesions with liquid nitrogen to reduce inflammation and promote healing.
Lifestyle Modifications: Guidance on skincare routines, diet adjustments, stress management, and avoiding triggers that exacerbate acne.